Installing GUI on Linux in the Cloud
We cloud computer we are able to create numerous services on the web at ease with only a fraction of the cost. Also, because cloud computer costs are only calculate when the computer is actually running, we can simply decommission the machine scale down the resources to help reduce cost and keep us within budget. Making use of this particular factor, bring great benefits to the deployment of your cloud solutions.
Cloud Configuration
We are going to have a quick look on how to set up a Linux system on the cloud. On this guide we are going to use the Cloud Provider Linode, which has great performance and great prices. Our computer will be running for the total cost of $5 p/month at the time of writing this article, so let’s crack on!
Software we need
- Linode Account
- Remote desktop client
- mRemoteNG (Windows)
- Remmina (Apple)
Set up Steps
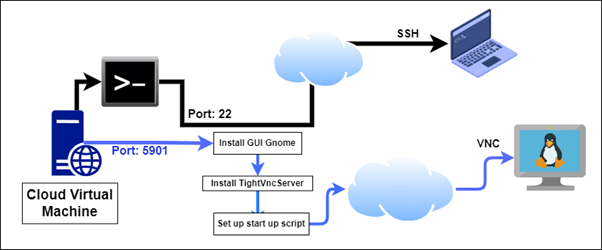
We are going to skip the deployment of the Linux machine on Linode and focus on the process of installing the required components on our Linux machine to establish a VNC (Virtual Network Connection) connection. VNC functions similarly to the Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP.)
Connect over ssh
ssh root@
Update and Upgrade your linux
sudo apt-update && apt-upgrade
Install a gui flavor, we are going for ubuntu-mate on this tutorial
apt install ubuntu-mate-desktop
Install VNC Server
apt install tightvncserver
Start the VNC Server check its working Asking to create a password for the connection (it has maximum 8 characters and will truncate the password if password is longer).
vncserver :1
Stop vncserver
vncserver -kill :1
After running vnc server for the first time, it has created a folder on the directories “.vnc” We are going to update the xstartup script file that will run as soon as the vnc server launches.
Configure VNC Server
cd ./vnc mv xstartup xstartup-bup nano xstartup
Create the following inside the xstartup
#!/bin/bash exec /usr/bin/mate-session &
Make new script executable
Chmod +x xstartup
Hardening Security
Create a lower privilege user
Its important we are not using the root account on a daily basis and are not logged directly to it. This is because in case you run any command you are running it with the highest privileges, and this is not something you want to do without thinking before hit run. Change default VNC port (5901) to something different
Create new user, so you are not logged as root
add user joker
Add user to sudoers file
usermode -aG sudo joker
Changing Default VNC Port
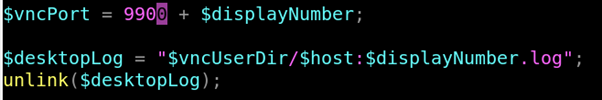
Specifies the TCP port on which Xvnc listens for connections from viewers (the protocol used in VNC is called RFB - "remote framebuffer"). The default is 5900 plus the display number.
Grep -n vncPort /usr/bin/vncserver
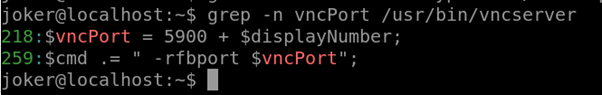
Vi /usr/bin/vncserver Inside vi jump into the line using the command :218
Managing VNC Server
Once you have it running unless you reboot your machine you will not have to start it again. Ideally you could create a bash script that is run at the moment the machine boots up, avoiding you to have to restart the server everytime you boot up your machine, this option will vary from environment to environment.
Check if server is running
ps aux | grep vnc
To start the sever
vncserver :1
Stop the server
vncserver -kill {display-number}
Wrapping up
You should now be able to connect to your machine using the VNC connection you have created. Now we can run our vncserver and connect to it using our remote desktop client.
-min.png)